CASE 141
1. What complications can occur after repair of tetralogy of Fallot? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Right ventricular enlargement
B. Right ventricular patch aneurysm
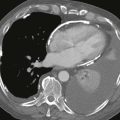
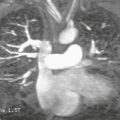
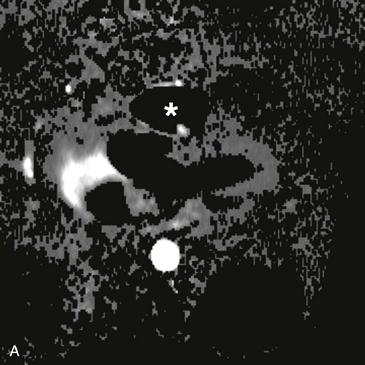
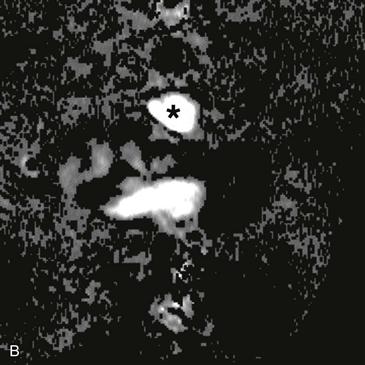
2. What structure is indicated by the asterisk (Figs. A and B)?
B. Aorta
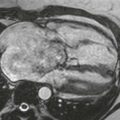
3. What complication is depicted by the images (Figs. A–C)?
A. Right ventricular enlargement
B. Right ventricular patch aneurysm.
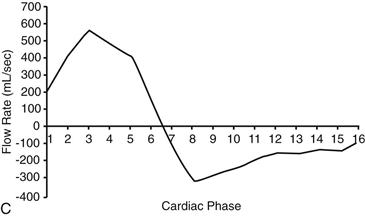
4. What MRI sequence was used to derive the flow curve?
A. Steady-state free precession
ANSWERS
Reference
Varaprasathan GA, Araoz PA, Higgins CB, et al. Quantification of flow dynamics in congenital heart disease: applications of velocity-encoded cine MR imaging. Radiographics. 2002;22(4):895–905. discussion 905–906.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 72, 363–367.
Comment
Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot
Patients with tetralogy of Fallot typically undergo repair during infancy or early childhood. Frequently, pulmonary infundibular stenosis is relieved by right ventriculoplasty. This procedure can cause long-term pulmonary valve insufficiency. Patients with pulmonary regurgitation may require replacement of the valve.
MRI
Velocity-encoded cine phase contrast images can be used to quantify regurgitation in the postoperative setting (Figs. A–C). MRI is an ideal method to evaluate pulmonary regurgitation because this modality is noninvasive, does not require ionizing radiation, evaluates the right ventricle more readily than echocardiography, and can accurately quantify pulmonary regurgitation and right ventricular volume. Cine MRI is employed for the quantitative appraisal of right ventricular function after surgery.