Reproductive/OB

Oxytocin (Pitocin)
CLASSIFICATION
Uterine smooth muscle stimulant
ACTIONS
Contracts uterine and mammary smooth muscle. Increases force, frequency, and duration of uterine contractions.
USES
• Managing incomplete or inevitable abortion
• Controlling postpartum hemorrhage
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Cephalopelvic disproportion, previous uterine surgery
• Unengaged fetal head, unfavorable fetal position or presentation
• Fetal distress without evidence of imminent delivery
• Placenta previa or cord prolapse or both
• Women with active genital herpes
PRECAUTIONS
• Used with great caution in women who are high parity (5 or more)
SIDE EFFECTS
• Tachycardia, premature ventricular contraction, hypotension
• Nausea, vomiting, water intoxication
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Frequently assess baseline vital signs, blood pressure, and fetal heart rate.*
2. *Constantly monitor frequency, duration, and strength of contractions.*
3. *Stop the infusion; notify the physician if the resting uterine pressure is above 15 to 20 mm Hg, if contractions are lasting longer than 1 minute, if they are occurring more frequently than every 2 to 3 minutes, or if an alteration in fetal heart rhythm or rate occurs.*
4. Maintain input and output; evaluate for excessive water retention.
5. Do not confuse with vasopressin (Pitressin), which is an antidiuretic hormone.
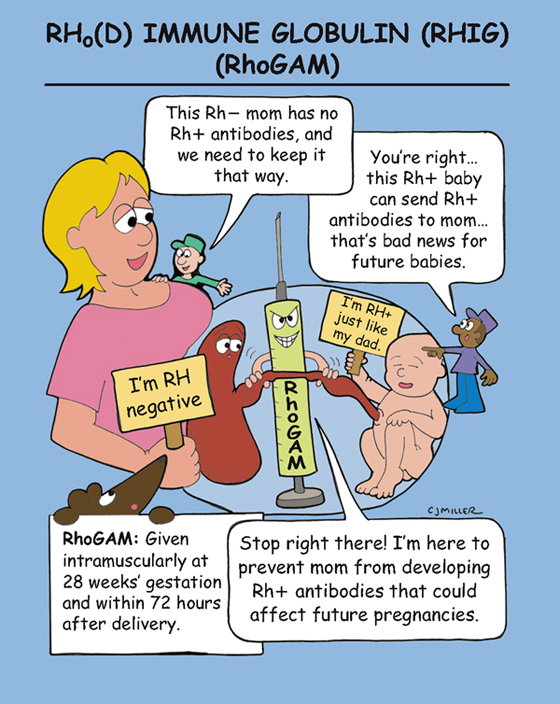
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (RhIG) (RhoGAM)
CLASSIFICATION
Immunosuppressant
ACTION
Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIG) is an immunoglobulin that is a concentrated preparation that contains antibodies to Rho(D). This prevents an Rh-negative woman from developing antibodies after exposure to Rho(D)-positive blood.
USES
• Prevents sensitization in Rh-negative pregnant patient given in the last trimester of pregnancy, as well as after abortion or miscarriage.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Not given to Rh-positive women.
SIDE EFFECTS
• Slight temperature elevation
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Administered intramuscularly at 28 weeks’ gestation and again within 72 hours after delive*ry.
2. *May also be administered to Rh-negative women receiving a blood transfusion or who have had a spontaneous or induced abortion or amniocentesis.*
3. ‡Instruct Rh-negative patients to advise health care providers of their Rh-negative status.‡
Anticholinergic Drugs for Overactive Bladder oxybutynin (Ditropan), solifenacin (VESIcare), tolterodine (Detrol)
CLASSIFICATION
Anticholinergic, muscarinic antagonists
ACTION
Block receptors in the bladder detrusor to relax bladder contractions.
USES
• To treat patients with an overactive bladder having symptoms of urinary frequency, urgency, or urge incontinence
PRECAUTIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Combined use with other anticholinergic medications will intensify the side effects.
• Urinary retention; bladder obstruction, benign prostatic hypertrophy
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Dry mouth; dry eyes,** blurred vision
• **Ditropan: urinary retention and hesitancy; tachycardia more common**
• **Constipation, gastric discomfort**
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Monitor for incontinence and postvoid residuals.*
2. ‡Teach patient how to use saline eye drops if dry eyes are a problem.‡
3. ‡Do not open or chew extended-release capsules.‡
4. ‡Teach behaviors to modify problem:‡
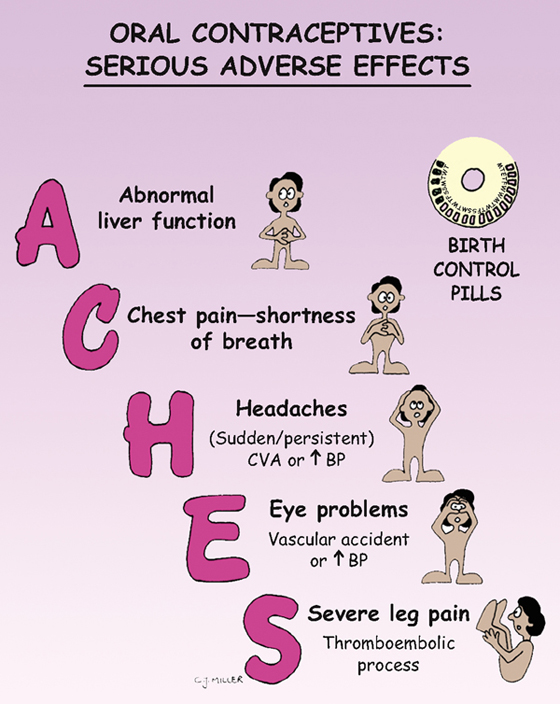
Oral Contraceptives: Serious Adverse Effects
ACTION
Combining of estrogen and progestin inhibits ovulation.
USES
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Pregnancy, history of thromboembolic disorders, cerebrovascular disease, coronary occlusion, breast cancer, abnormal liver function, abnormal vaginal bleeding, smokers over age of 35 years
PRECAUTIONS
• Women who have diabetes, hypertension, cardiac disease, gallbladder problems, epilepsy, and migraine headaches
SIDE EFFECTS
• Minor: **breast tenderness, nausea, bloating, edema, weight gain**
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. Patient can take oral contraceptives immediately after delivery for birth control if she is not breast-feeding.
2. ‡Encourage an annual pelvic examination and Papanicolaou (Pap) smear.‡
3. ‡If patient misses a pill, she can take it with the next scheduled dose. If patient misses two doses, she can take two doses per day on the following 2 days. If patient misses three doses, she can initiate a new cycle (starting 7 days after she took the last pill). Teach patient to use another form of birth control during this time.‡
4. ‡The patient should take pills at the same time each day (e.g., with a meal, at bedtime).‡
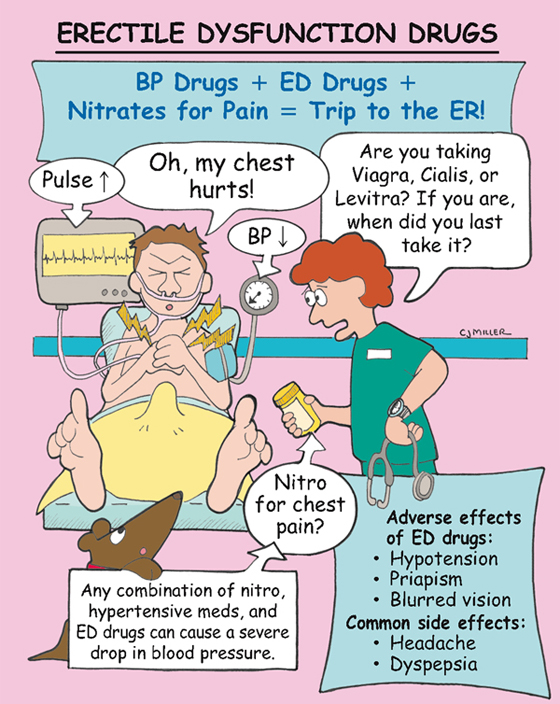
Erectile Dysfunction Drugs
ACTIONS
PDE5 inhibitors increase arterial pressure, reduce venous outflow in the penis, thereby causing engorgement to produce and/or enhance an erection. It only enhances the normal erectile response to sexual stimuli. In the absence of stimuli, no erection occurs.
USES
• Organic, psychogenic, mixed cause origin of erectile dysfunction (ED)
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Do not take within 24 hours of taking nitrate medication.
• Patients taking alpha-blocker medications.
• Use with caution when taking with alpha blockers for treatment of prostatic hypertrophy (Viagra).
• Dose may be reduced when patients take verapamil and diltiazem.
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Severe hypotension when used within 24 hours of nitrates**
• **Dyspepsia, headache, nasal congestion**
• vardenafil (Levitra): use caution with medications that cause a prolonged QT interval
• Viagra—†erection lasting longer than 4 to 6 hours (priapism)†
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. ‡Instruct patients taking cardiac medications to consult with the health care provider about the safe use of ED drugs.‡
2. *Ask male patients who are complaining of chest pain if they have taken an ED drug within the last 48 hours.*
3. ED drugs can be taken by men who are healthy enough for normal sexual activity.
4. ‡Viagra: Instruct patient to report erections lasting longer than 4 hours to a health care provider.‡
5. Tadalafil (Cialis) has a 36-hour duration of action; other ED drugs have a 4-hour duration.