CASE 14
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis for a precontrast T1 hyperintense cardiac mass? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Lipoma
B. Lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum
E. Myxoma
2. What is the most common presentation for this entity?
A. Arrhythmia
C. Asymptomatic
D. Superior vena cava obstruction
3. What is the composition of this lesion?
B. Intracellular methemoglobin
C. Melanin
D. Fat
4. What is the appropriate management in an asymptomatic patient?
A. Do nothing
ANSWERS
Reference
Gaerte SC, Meyer CA, Winer-Muram HT, et al. Fat-containing lesions of the chest. Radiographics. 2002;22 Spec No:S61–S78.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 281–282.
Comment
Imaging
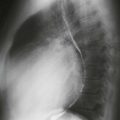
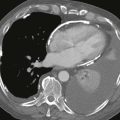
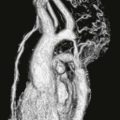
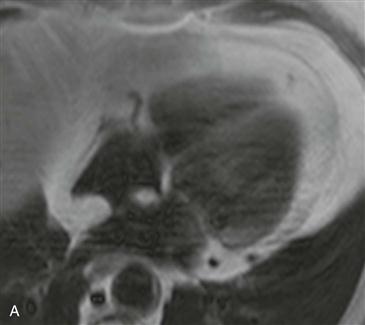
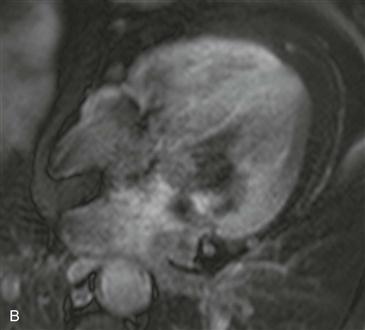
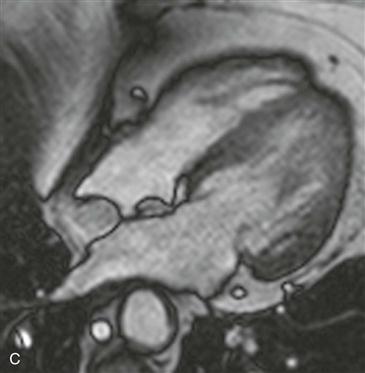
Axial black blood T1-weighted images without and with fat suppression show a fat density mass within the interatrial septum (Figs. A and B). There is sparing in the region of the fossa ovalis giving rise to a dumbbell shape of the lesion (Fig. C). These features are diagnostic of lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum.
Diagnosis
Lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum is a benign condition that is usually incidentally discovered on imaging performed for other reasons. It represents an abnormal deposition of fat within the atrial septum that is greater than 2 cm in transverse dimension. It is more common in older women and obese patients. Echocardiography occasionally mistakes this entity for a cardiac mass. Diagnosis is easily made with either CT or MRI. The location and lesion shape differentiate it from cardiac lipoma and physiologic myocardial fat. Rarely, patients are symptomatic and present with arrhythmia.