CASE 138
History: No patient history is available.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis for dilation of the azygos vein? (Choose all that apply.)
B. Interruption of inferior vena cava
D. Superior vena cava obstruction
2. What is the most likely diagnosis?
B. Interruption of inferior vena cava
D. Superior vena cava obstruction
3. Which complex of anomalies is associated with this finding?
A. Polysplenia
B. Asplenia
D. Situs solitus with levocardia
4. The polysplenia syndrome is highly associated with all of the following features except:
ANSWERS
CASE 138
References
Bass JE, Redwine MD, Kramer LA, et al. Spectrum of congenital anomalies of the inferior vena cava: cross-sectional imaging findings. Radiographics. 2000;20(3):639–652.
Jelinek JS, Stuart PL, Done SL, et al. MRI of polysplenia syndrome. Magn Reson Imaging. 1989;7(6):681–686.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 307–309.
Comment
Anatomy
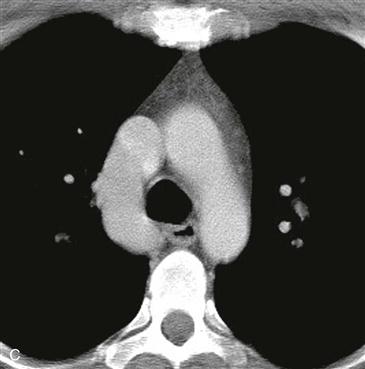
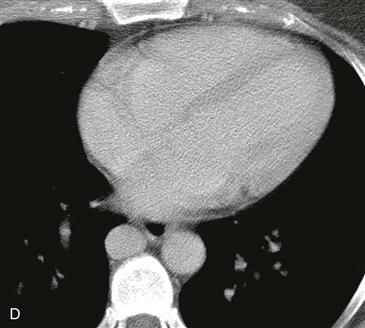
In this anomaly, the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava is interrupted. Typically, the blood passes through collateral channels to enter the azygos or hemiazygos vein. The hepatic veins drain separately into the right atrium. The anomaly may be isolated, as in this case, or it may be associated with polysplenia syndrome which is a type of heterotaxia.
Imaging
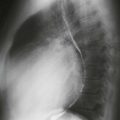
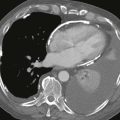
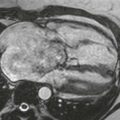
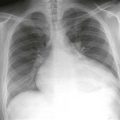
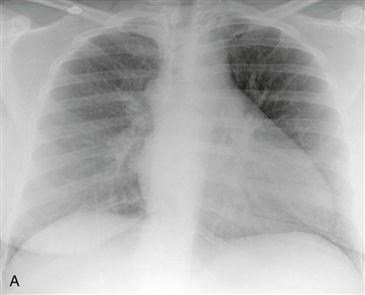
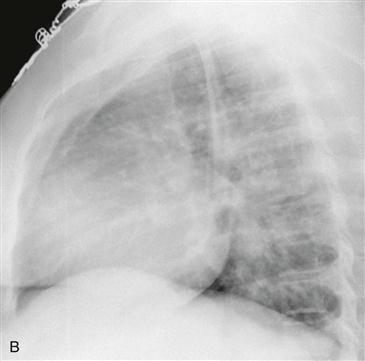
Radiography typically demonstrates marked enlargement of the azygos vein (Fig. A). The lateral view may show no inferior vena cava shadow just above the diaphragm (Fig. B). CT and MRI can be performed to evaluate the vascular anatomy and to identify any associated anomalies (Figs. C and D).
Heterotaxia Syndromes
There are two types of heterotaxia syndromes: bilateral right-sidedness (asplenia syndrome) and bilateral left-sidedness (polysplenia syndrome). Patients with asplenia syndrome generally present early in life with cyanosis and complex congenital heart disease (e.g., transposition of the great arteries, double outlet right ventricle, common atrioventricular valve). Patients with polysplenia syndrome present later in life with less severe congenital heart defects (e.g., atrial septal defect, partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection). More than 70% of all patients with polysplenia have either azygos or hemiazygos continuation of the IVC.