CASE 137
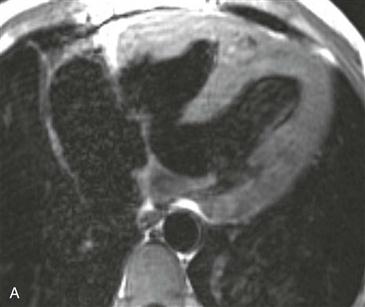
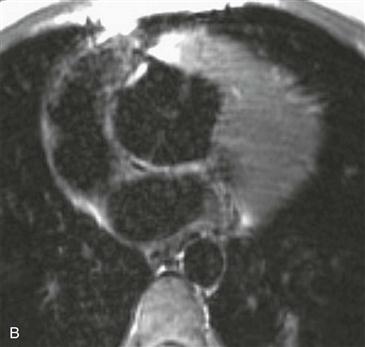
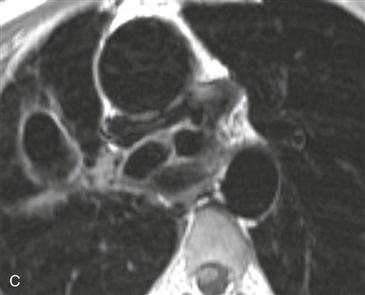
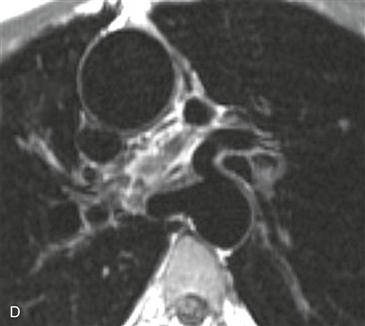
History: A patient has dyspnea on exertion.
1. What findings are seen? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Right ventricular hypertrophy
C. Pulmonary infundibular stenosis
D. Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
2. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Atrioventricular septal defect
C. Transposition of the great arteries.
3. How do the lungs receive blood?
A. Aorta-to-pulmonary artery collaterals
C. Retrograde flow through pulmonary veins
D. Arteriovenous malformations.
ANSWERS
Reference
Reddy GP, Higgins CB. Magnetic resonance imaging of congenital heart disease: evaluation of morphology and function. Semin Roentgenol. 2003;38(4):342–351.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 362–363.
Comment
Anomalies of Tetralogy of Fallot
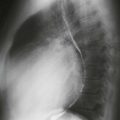
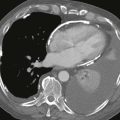
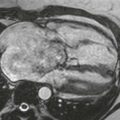
Pulmonary atresia with VSD is a severe variant of tetralogy of Fallot. In the past, it was sometimes called “pseudotruncus,” but this anomaly is not a form of truncus arteriosus. The central pulmonary arteries are frequently hypoplastic, and the peripheral pulmonary arteries are often stenotic.
MRI
MRI is optimal for assessing the pulmonary arteries because it evaluates supracardiac structures more readily than echocardiography. Also, MRI does not rely on contrast enhancement to show the vessels, as does cineangiography (Figs. A–D); this is especially useful because the pulmonary arteries usually do not opacify well in the presence of pulmonary atresia.