CASE 134
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis based on the history? (Choose all that apply.)
B. Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
D. Transposition of the great arteries
2. Which type of VSD is depicted by the images?
A. Muscular
D. Supracristal
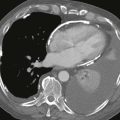
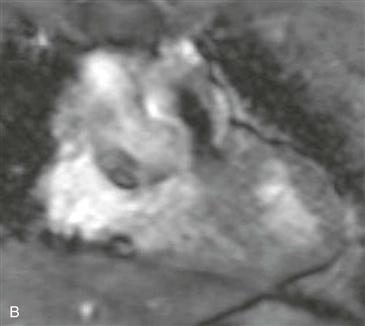
3. In Fig. B, what does the black jet indicate?
4. Which abnormality is not associated with a supracristal VSD?
ANSWERS
Reference
Bremerich J, Reddy GP, Higgins CB. MRI of supracristal ventricular septal defects. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999;23(1):13–15.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, p 60.
Comment
Description of Anomaly
A supracristal VSD is also known as a doubly committed subarterial defect because its location is both subaortic and subpulmonary.
Imaging
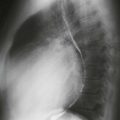
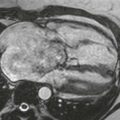
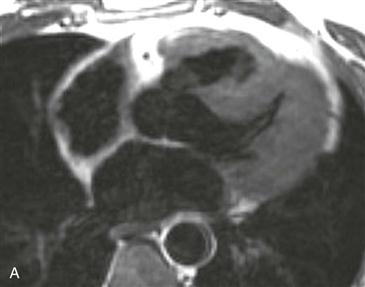
Echocardiography is the primary imaging modality for the evaluation of intracardiac shunts. However, because of the location of a supracristal VSD, it may be difficult to assess with echocardiography. MRI demonstrates the characteristic appearance of a connection between the aortic root and right ventricular outflow tract (Fig. A). Steady-state free precession cine images can demonstrate a spin dephasing artifact (black flow jet) directed across the VSD into the pulmonary outflow tract, indicating a left-to-right shunt (Fig. B).