CASE 131
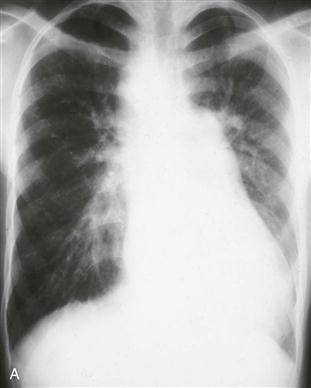
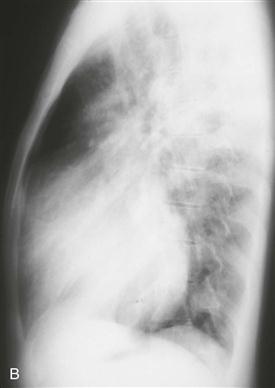
History: A patient presents with cyanosis.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis in a patient with cyanosis and increased pulmonary vascularity? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Transposition of the great arteries
B. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
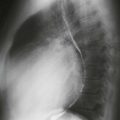
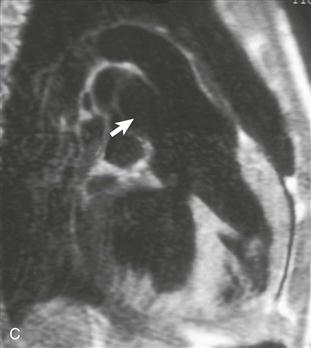
2. What structure is indicated by the arrow in Fig. C?
C. Aortic arch
3. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Transposition of the great arteries
B. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
4. What other cyanotic heart disease is most strongly associated with a right aortic arch?
A. Transposition of the great arteries
ANSWERS
Reference
Johnson TR. Conotruncal cardiac defects: a clinical imaging perspective. Pediatr Cardiol. 2010;31(3):430–437.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 324–327.
Comment
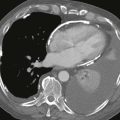
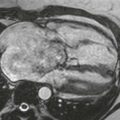
Anatomy and Clinical Features
Truncus arteriosus is a cyanotic admixture lesion in which the pulmonary artery and aorta arise from a common trunk. There may be a main pulmonary artery, but in some patients the right and left pulmonary arteries arise separately from the common trunk. A ventricular septal defect is present. The truncal valve usually is tricuspid but can have four or more leaflets. Approximately 30% to 35% of patients have a mirror-image right aortic arch.