CHAPTER 13 Muscle Relaxants and Monitoring of Relaxant Activity
1 Describe the anatomy of the neuromuscular junction
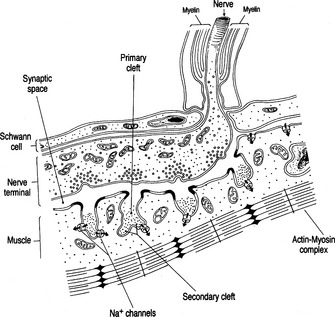
A motor nerve branches near its terminus to contact many muscle cells, losing myelin to branch further and come into closer contact with the junctional area of the muscle surface. Within the most distal aspect of the motor neuron, vesicles containing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) can be found. The terminal neuron and muscle surface are loosely approximated with protein filaments, and this intervening space is known as the junctional cleft. Also contained within the cleft is extracellular fluid and acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme responsible for metabolizing ACh. The postjunctional motor membrane is highly specialized and invaginated, and the shoulders of these folds are rich in ACh receptors (Figure 13-1).
3 With regard to neuromuscular transmission, list all locations for acetylcholine receptors
ACh receptors are found in several areas:
 About 5 million ACh receptors per neuromuscular junction (NMJ) are located on the postjunctional motor membrane.
About 5 million ACh receptors per neuromuscular junction (NMJ) are located on the postjunctional motor membrane.4 Review the steps involved in normal neuromuscular transmission
 ACh is released from storage vesicles at the nerve terminal. Enough ACh is released to bind 500,000 receptors.
ACh is released from storage vesicles at the nerve terminal. Enough ACh is released to bind 500,000 receptors. ACh molecules bind to the α-subunits of the ACh receptor on the postjunctional membrane, generating a conformational change and opening receptor channels. Receptors do not open unless both α-receptors are occupied by ACh (a basis for the competitive antagonism of nondepolarizing relaxants).
ACh molecules bind to the α-subunits of the ACh receptor on the postjunctional membrane, generating a conformational change and opening receptor channels. Receptors do not open unless both α-receptors are occupied by ACh (a basis for the competitive antagonism of nondepolarizing relaxants).6 How are muscle relaxants classified?
 Depolarizing relaxants: Succinylcholine (SCH) is two molecules of ACh bound together, an agonist at the NMJ, and the only depolarizing relaxant available clinically. As such, SCH binds to the α-subunits of the ACh receptor. After binding, SCH can open the ion channel and depolarize the end plate. Although SCH, like ACh, binds only briefly to the receptor, it is not hydrolyzed in the synaptic cleft by acetylcholinesterase. In fact, SCH molecules may unbind and rebind receptors repeatedly. SCH must diffuse away and be broken down in the plasma by enzymes called plasma- or pseudocholinesterase, and time for clearance from the body is an accurate measure of its duration of effect.
Depolarizing relaxants: Succinylcholine (SCH) is two molecules of ACh bound together, an agonist at the NMJ, and the only depolarizing relaxant available clinically. As such, SCH binds to the α-subunits of the ACh receptor. After binding, SCH can open the ion channel and depolarize the end plate. Although SCH, like ACh, binds only briefly to the receptor, it is not hydrolyzed in the synaptic cleft by acetylcholinesterase. In fact, SCH molecules may unbind and rebind receptors repeatedly. SCH must diffuse away and be broken down in the plasma by enzymes called plasma- or pseudocholinesterase, and time for clearance from the body is an accurate measure of its duration of effect.8 If succinylcholine works so rapidly and predictably, why not use it all the time?
SCH has numerous side effects:
 SCH stimulates both nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Stimulation of muscarinic receptors within the sinus node results in numerous bradyarrhythmias, including sinus bradycardia, junctional rhythms, ventricular escape and asystole.
SCH stimulates both nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Stimulation of muscarinic receptors within the sinus node results in numerous bradyarrhythmias, including sinus bradycardia, junctional rhythms, ventricular escape and asystole. Prolonged exposure of the receptors to SCH results in persistent open receptor channel and ionic fluxes through the ion pore, known as phase II or desensitization blockade. Normal depolarization/repolarization is not possible until SCH is metabolized.
Prolonged exposure of the receptors to SCH results in persistent open receptor channel and ionic fluxes through the ion pore, known as phase II or desensitization blockade. Normal depolarization/repolarization is not possible until SCH is metabolized. In patients ambulatory soon after surgery, random generalized muscle contractions (fasciculations) have been associated with painful myalgias. Whether pretreating with a subparalyzing dose of a nondepolarizing relaxant before SCH is effective in reducing myalgias continues to be a matter of debate.
In patients ambulatory soon after surgery, random generalized muscle contractions (fasciculations) have been associated with painful myalgias. Whether pretreating with a subparalyzing dose of a nondepolarizing relaxant before SCH is effective in reducing myalgias continues to be a matter of debate. SCH increases ICP. The etiology is not completely understood, but it is known that a subparalyzing dose of a nondepolarizing relaxant before SCH administration reduces the increase in ICP; thus perhaps fasciculations are the cause of the increase in ICP.
SCH increases ICP. The etiology is not completely understood, but it is known that a subparalyzing dose of a nondepolarizing relaxant before SCH administration reduces the increase in ICP; thus perhaps fasciculations are the cause of the increase in ICP. In the presence of immature extrajunctional receptors, administration of SCH may result in severe hyperkalemia and malignant ventricular arrhythmias. Extrajunctional receptors are normally suppressed by activity. Any condition that decreases motor-nerve activity results in a proliferation of these receptors. Examples include spinal cord and other denervation injuries, upper and lower motor neuron disease, closed head injuries, burns, neuromuscular diseases, and even prolonged immobility.
In the presence of immature extrajunctional receptors, administration of SCH may result in severe hyperkalemia and malignant ventricular arrhythmias. Extrajunctional receptors are normally suppressed by activity. Any condition that decreases motor-nerve activity results in a proliferation of these receptors. Examples include spinal cord and other denervation injuries, upper and lower motor neuron disease, closed head injuries, burns, neuromuscular diseases, and even prolonged immobility. SCH increases intraocular pressure (IOP). There is a theoretic risk for the use of SCH in patients with open eye injury (i.e., extrusion of extraocular contents). However, the increases in IOP are modest, and from a clinical perspective extrusion of ocular contents has not been observed. Certainly if a nondepolarizing agent is administered instead of SCH and the patient is intubated before optimal intubating conditions, coughing on the endotracheal tube (called “bucking”) increases IOP significantly and puts the patient at risk for extruding ocular contents.
SCH increases intraocular pressure (IOP). There is a theoretic risk for the use of SCH in patients with open eye injury (i.e., extrusion of extraocular contents). However, the increases in IOP are modest, and from a clinical perspective extrusion of ocular contents has not been observed. Certainly if a nondepolarizing agent is administered instead of SCH and the patient is intubated before optimal intubating conditions, coughing on the endotracheal tube (called “bucking”) increases IOP significantly and puts the patient at risk for extruding ocular contents.11 Review the properties of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants
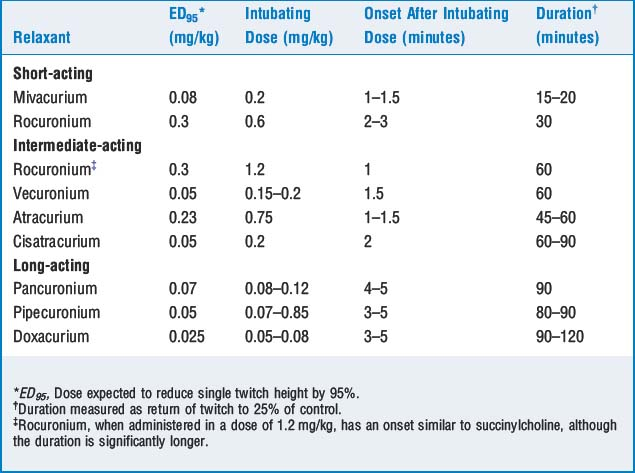
Nondepolarizing relaxants are competitive antagonists at the NMJ and are classified by their duration of action (short-, intermediate-, and long-acting). The doses, onset, and duration of effect are described in Table 13-1.
12 Review the metabolism of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers
 Aminosteroid relaxants (e.g., pancuronium, vecuronium, pipecuronium, and rocuronium) are diacetylated in the liver, and their action may be prolonged in the presence of hepatic dysfunction. Vecuronium and rocuronium also have significant biliary excretion, and their action may be prolonged with extrahepatic biliary obstruction.
Aminosteroid relaxants (e.g., pancuronium, vecuronium, pipecuronium, and rocuronium) are diacetylated in the liver, and their action may be prolonged in the presence of hepatic dysfunction. Vecuronium and rocuronium also have significant biliary excretion, and their action may be prolonged with extrahepatic biliary obstruction. Relaxants with significant renal excretion include tubocurarine, metocurine, doxacurium, pancuronium, and pipecuronium.
Relaxants with significant renal excretion include tubocurarine, metocurine, doxacurium, pancuronium, and pipecuronium.14 Review medications that potentiate the actions of muscle relaxants
 Volatile anesthetics potentiate relaxants for a number of reasons, including central nervous system depression, increasing blood flow (and relaxant molecules) to muscle, and desensitization of the postjunctional membrane.
Volatile anesthetics potentiate relaxants for a number of reasons, including central nervous system depression, increasing blood flow (and relaxant molecules) to muscle, and desensitization of the postjunctional membrane. Local anesthetics affect the prejunctional, postjunctional, and motor membranes, depressing normal functions at all these sites.
Local anesthetics affect the prejunctional, postjunctional, and motor membranes, depressing normal functions at all these sites. Calcium channel and β-adrenergic blockers impair ion transport, but the clinical significance at the NMJ is probably not important.
Calcium channel and β-adrenergic blockers impair ion transport, but the clinical significance at the NMJ is probably not important. Antibiotics, and most notably aminoglycosides, appear to have negative prejunctional and postjunctional effects. Penicillin and cephalosporins do not affect relaxant activity.
Antibiotics, and most notably aminoglycosides, appear to have negative prejunctional and postjunctional effects. Penicillin and cephalosporins do not affect relaxant activity. Magnesium inhibits the release and the depolarizing effect of ACh and decreases muscle fiber excitability. Lithium also potentiates neuromuscular blockade.
Magnesium inhibits the release and the depolarizing effect of ACh and decreases muscle fiber excitability. Lithium also potentiates neuromuscular blockade.19 Which mode is most commonly used to assess degree of blockade? How is it done?
KEY POINTS: Muscle Relaxants 
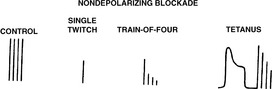
25 What are the characteristic responses to the various patterns of stimulation produced by nondepolarizing agents?
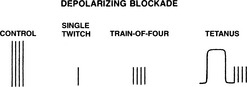
26 Summarize the characteristic responses to the various patterns of stimulation produced by depolarizing relaxants (succinylcholine)
The single-twitch, TOF, and tetanus amplitudes are uniformly decreased at any level of blockade. There is lack of fade in response to TOF and tetanus and lack of posttetanic facilitation. A desensitization or phase II blockade may develop with prolonged exposure to SCH. Phase II blockade has the same twitch characteristics as nondepolarizing blockade (Figure 13-3).
35 Review the clinical signs associated with return of adequate strength
| Test | Results | Percentage of Receptors Occupied |
|---|---|---|
| Tidal volume | >5 ml/kg | 80 |
| Single twitch | Return to baseline | 75–80 |
| Train of four | No fade | 70–75 |
| Sustained tetanus (50 Hz, 5 seconds) | No fade | 70 |
| Vital capacity | >20 ml/kg | 70 |
| Double-burst stimulation | No fade | 60–70 |
| Sustained tetanus (100 Hz, 5 seconds) | No fade | 50 |
| Inspiratory force | >−40 cm H2O | 50 |
| Head lift | Sustained 5 seconds | 50 |
| Hand grip | Return to baseline | 50 |
| Sustained bite | Sustained clenching of a tongue depressor | 50 |
36 A patient appears weak after pharmacologic reversal of neuromuscular blockade. What factors should be considered?
1. Herrerling T.M., Le N. Brief review: Neuromuscular monitoring: an update for clinician. Can J Anesth. 2007;54:58-72.
2. Hirsch N.P. Neuromuscular junction in health and disease. Br J Anaesth. 2007;99:132-138.
3. Martyn J.A.J., Richtsfeld M. Succinylcholine-induced hyperkalemia in acquired pathologic states. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:158-169.
4. Naguib M. Sugammadex: Another milestone in clinical neuromuscular pharmacology. Anesth Analg. 2007;104:575-581.