CASE 13
History: No patient history is available.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Amyloidosis
D. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
2. What is the main myocardial finding?
D. Basal interventricular septal hypertrophy
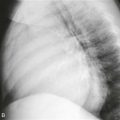
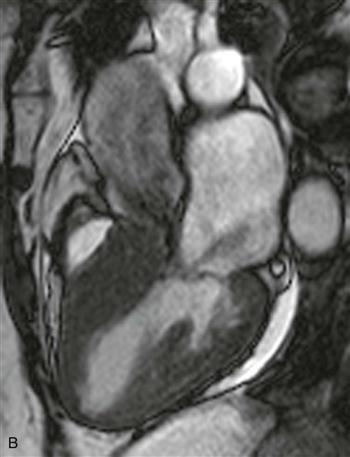
3. At what level is the aortic stenosis (Fig. B)?
A. Subaortic
B. Valvular
D. No evidence of aortic stenosis
4. What is the most common variant of HCM?
A. Concentric
B. Apical
D. Masslike
ANSWERS
CASE 13
Reference
Chun EJ, Choi SI, Jin KN, et al. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: assessment with MR imaging and multidetector CT. Radiographics. 2010;30(5):1309–1328.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 284–288.
Comment
Imaging
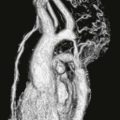
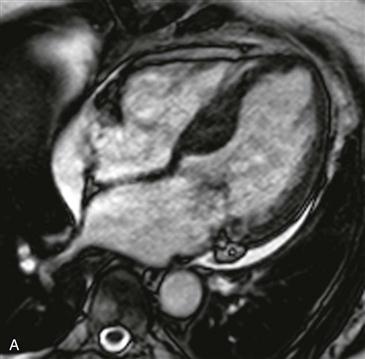
Cine steady-state free precession (SSFP) four-chamber view shows basal interventricular septal hypertrophy (Fig. A). Cine SSFP left ventricular outflow tract view shows flow void jets of mitral regurgitation and aortic stenosis (Fig. B). These findings are consistent with the asymmetric form of HCM. This diagnosis should be made only in the absence of a systemic condition that could cause myocardial hypertrophy.
Diagnosis
HCM is an inherited cardiomyopathy characterized histologically by myocyte disarray and interstitial fibrosis. These histologic findings lead to an increased risk for fatal arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death. Echocardiography is the standard screening modality for patients suspected to have HCM. MRI is used in difficult cases, in unusual patterns of HCM, and in patients who are candidates for invasive therapy. MRI is superior in assessing left ventricular function and in determining the overall risk for sudden cardiac death. This case shows the most common HCM phenotype, asymmetric septal hypertrophy. Asymmetric HCM is diagnosed when a portion of the septum measures 15 mm or more at end-diastole. There are two clinically important subtypes of asymmetric HCM—obstructive and nonobstructive forms. The obstructive form is characterized by dynamic left ventricular outflow obstruction caused by the hypertrophied septum or systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve. Patients with obstructive HCM should be evaluated for possible intervention using septal alcohol ablation or surgical myectomy.
Prognostic Indicators
MRI is a useful prognostic indicator for risk of sudden cardiac death. Specific imaging findings that indicate an increased risk include the following: