CASE 121
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis for a cardiac mass? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Thrombus
B. Angiosarcoma
C. Myxoma
2. What is the most common cardiac mass?
A. Thrombus
B. Benign primary cardiac tumor
C. Malignant primary cardiac tumor
D. Metastasis
3. Which imaging finding is more suggestive of a benign cardiac tumor?
B. Lung nodules
C. Involvement of one cardiac chamber
D. Extension outside the heart
4. What is the most likely diagnosis given the absence of a known primary?
A. Liposarcoma
B. Thrombus
C. Myxoma
D. Angiosarcoma
ANSWERS
CASE 121
References
Berry MF, Williams M, Welsby I, et al. Cardiac angiosarcoma presenting with right coronary artery pseudoaneurysm. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2010;24(4):633–635.
Randhawa K, Ganeshan A, Hoey ET. Magnetic resonance imaging of cardiac tumors: part 2, malignant tumors and tumor-like conditions. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2011;40(4):169–179.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, pp 281–282.
Comment
Epidemiology and Prognosis
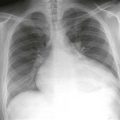
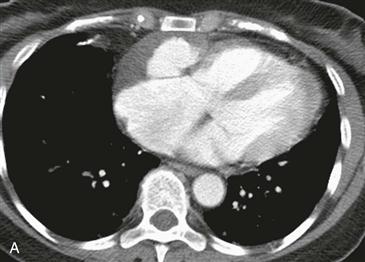
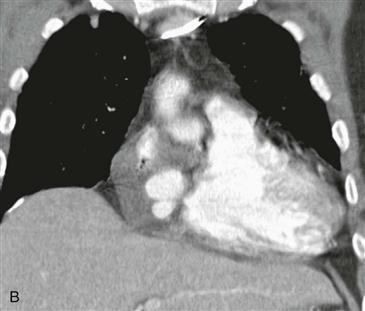
Most cardiac tumors (98%) are metastases from extracardiac primaries. Angiosarcoma is the most common primary malignant cardiac tumor. It is usually an infiltrative right atrial free wall mass. It often extends outside the heart and may involve more than one cardiac chamber. Rarely, it can lead to a right coronary artery pseudoaneurysm as shown in this case. Prognosis is poor with median survival less than 1 year in patients with metastatic disease.
Imaging
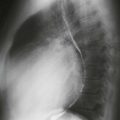
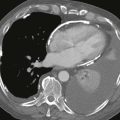
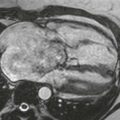
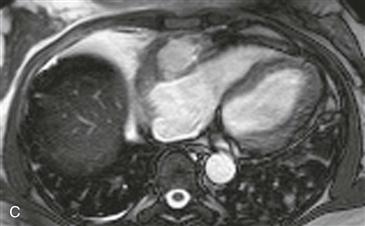
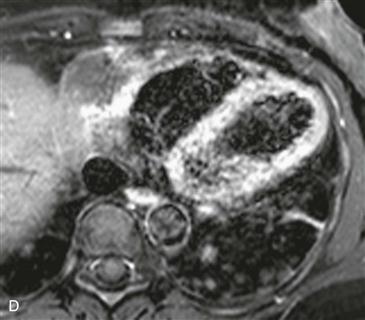
Cardiac CT images (Figs. A and B) show an infiltrative mass involving the free wall of the right atrium and right ventricle. Within the mass is a round collection of contrast material, which is separate from the cardiac chambers located in the right atrioventricular groove. An axial bright blood image shows right atrial free wall thickening and a right coronary artery pseudoaneurysm (Fig. C). A black blood image obtained after gadolinium administration (Fig. D) shows enhancement of the right atrial free wall mass. This patient had multiple pulmonary nodules, and biopsy of these yielded a diagnosis of angiosarcoma.