Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
ACTIONS
SSRIs decrease the reuptake of serotonin at selected nerve terminals in the central nervous system and increase serotonin activity at the nerve synapse. Increased availability of serotonin at the receptors results in mood elevation and reduced anxiety.
USES
• Obsessive-compulsive disorder
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
SIDE EFFECTS
• Nausea, insomnia, weight gain
• **Sexual dysfunction: decreased libido, impotence, delayed ejaculation, delayed or absent orgasm**
• Hyponatremia, neonatal withdrawal, increased risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding
• Serotonin syndrome: agitation, confusion, disorientation, hallucinations
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. †Treatment of depression places the patient at increased risk for suicide; monitor patient for mood changes.†
2. ‡Do not stop taking medication; withdrawal should be gradual, not abrupt.‡
4. *Bleeding problems may occur if used concurrently with anticoagulants or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).*
5. ‡Teach patient and family about the side effects, and advise them to notify the health care provider if any symptoms occur.‡
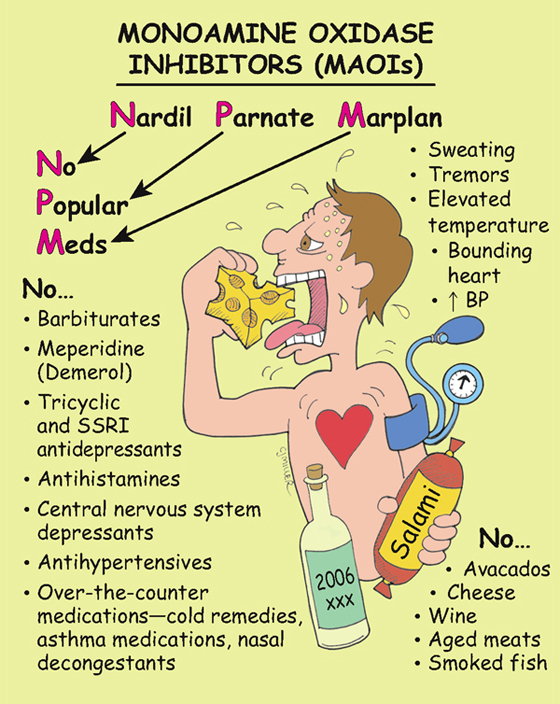
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
CLASSIFICATION
Antidepressant
ACTION
The antidepressant effects of the MAOIs are the result of blocking monoamine oxidase in nerve terminals. This action increases the availability and concentration of norepinephrine and serotonin for neurotransmission.
USES
• MAOIs are reserved for patients who are depressed and have not responded to tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Impaired renal or hepatic function
• Cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease or both
PRECAUTIONS
• *Hypertensive crisis can be triggered by eating foods rich in tyramine (pickled, aged, caffeinated, or fermented food or drinks and medications containing diuretics, antihistamines, antihypertensives, and ephedrine).*
• MAOIs interact with many medications.
SIDE EFFECTS
• Central nervous system stimulation: anxiety, agitation, hypomania, mania
• **Headache, dry mouth, lethargy**
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. ‡Advise patient to avoid over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, especially cold remedies, nasal decongestants, and asthma medications.‡
2. ‡Advise patients to tell all health care professionals they are taking an MAOI.‡
3. Assess patient for changes in mood; evaluate suicidal tendencies.
4. Determine if patient needs help with dosing or is capable of self-dosing.
5. ‡Teach patient to avoid tyramine-rich foods that can lead to hypertensive crisis (fermented meats [smoked sausage, pepperoni, salami], dried or cured fish, all cheese, Chianti wine, dietary supplements with protein extract, soy sauce), ripe avocados.‡
6. Patient should also avoid chocolate and caffeinated beverages.
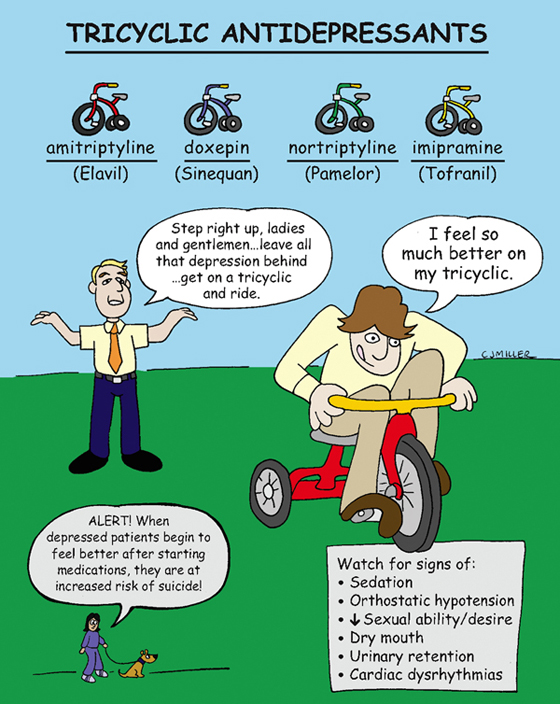
Tricyclic Antidepressants
ACTION
Block the reabsorption of norepinephrine and serotonin, which allows more of the neurotransmitters to be available at postsynaptic receptors.
USES
• Depression: alcohol and drug withdrawal, major depression
• Bipolar disorder (manic-depressive)
• Often used for patients who fail to respond well to other antidepressants
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Acute recovery phase of severe coronary artery disease
• Not administered within 14 days of taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
PRECAUTIONS
• History of suicidal behavior or ideations
• Hyperthyroidism; cardiac, renal, hepatic disease
• Problems with urinary retention (benign prostatic hypertrophy [BPH]) or history of seizures
SIDE EFFECTS
• Sedation, especially during first few weeks; **orthostatic hypotension**
• **Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, headache, urinary retention, blurred vision, tachycardia**
• Cardiac toxicity: decreases vagal influence; and slow conduction †(dysrhythmias)†
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. ‡Teach patients how to manage orthostatic hypotension; notify health care provider for persistent low blood pressure or rapid pulse.‡
2. Administer at bedtime to minimize problems with sedation.
3. Advise patient to stop smoking and to avoid alcohol.
4. ‡Therapy usually continues for a minimum of 6 months; do not abruptly stop taking medication or a relapse may occur.‡
5. *When depressed patient begins to feel better, the risk of suicide increases; monitor patient closely for mood changes or unusual changes in behavior.*
6. Beneficial effects will not peak for several weeks.
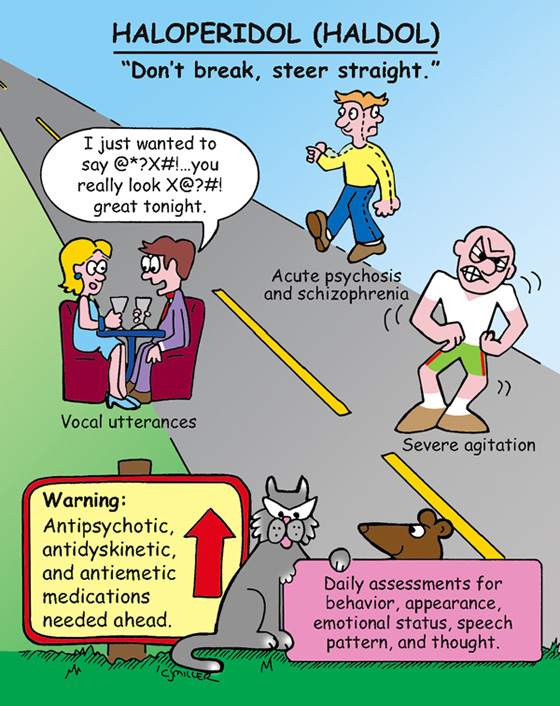
Haloperidol (Haldol)
ACTION
A first-generation antipsychotic that blocks receptors for dopamine within the central nervous system (CNS), as well as outside the CNS.
USES
• Schizophrenia, acute psychosis, Tourette syndrome
• Sedation of patients who are severely agitated
PRECAUTIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Parkinson disease (will counteract effectiveness of Parkinson medications and increase the symptoms)
• CNS depression, narrow-angle glaucoma, severe cardiac and hepatic disease
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Extrapyramidal reactions**
• **Tardive dyskinesia (late, twisting movement of face and tongue; “lip smacking”)**
• **Parkinsonism (bradykinesia, masklike facies, drooling, tremor, gait problems)**
• **Acute dystonia (spasms of tongue, face, neck, and back)**
• **Akathisia (compulsive restless movement, anxiety, agitation)**
• †Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (rare but serious)†
• **Anticholinergic effects: drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention**
• **QT changes and potential for** †dysrhythmias†
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Frequently monitor patient for reduction of target symptoms.*
2. *Routinely assess for presence of involuntary movement.*
3. *Provide family and patient education; poor adherence is common cause of therapeutic failure.*
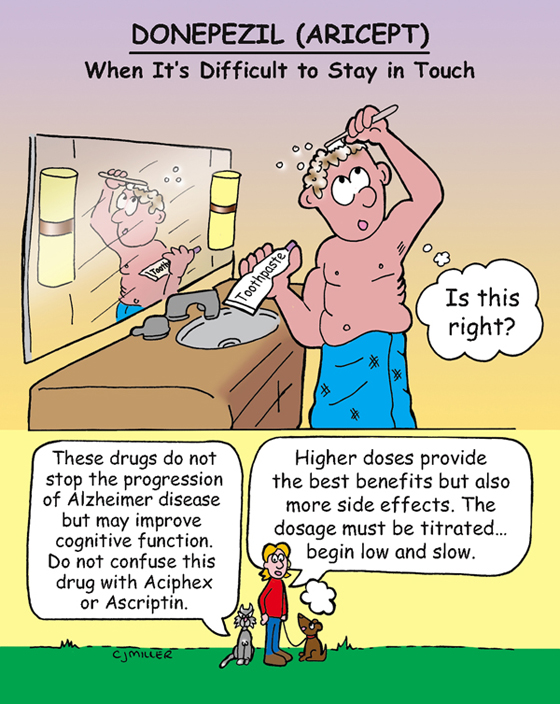
Donepezil (Aricept, Aricept ODT)
CLASSIFICATION
Cholinesterase inhibitor (cholinergic)
ACTIONS
Inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine (ACh) by cholinesterase (AChE). This breakdown increases the availability of ACh for improved nerve transmission by the central cholinergic neurons. It is selective for brain neurons.
USES
• Slows progression of Alzheimer disease; does not stop progression or affect the underlying disease process.
PRECAUTIONS
• Patients with chronic airway problems may experience bronchoconstriction caused by increased levels of Ach.
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Gastrointestinal (GI): nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, diarrhea**
• †Toxic effects: cholinergic crisis;† *atropine is antidote for cholinergic crisis*
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. Obtain baseline assessment to determine response to medication.
2. *Assess for urinary obstruction and monitor for difficulty urinating, especially in older men.*
3. Monitor for respiratory airway compromise and bradycardia.
4. *Oral disintegrating tablet should be placed under the tongue, not chewed or swallowed.*
5. ‡Teach family the drug is not a cure but only slows progression of symptoms.‡