CHAPTER 12 Intravenous Anesthetics and Benzodiazepines
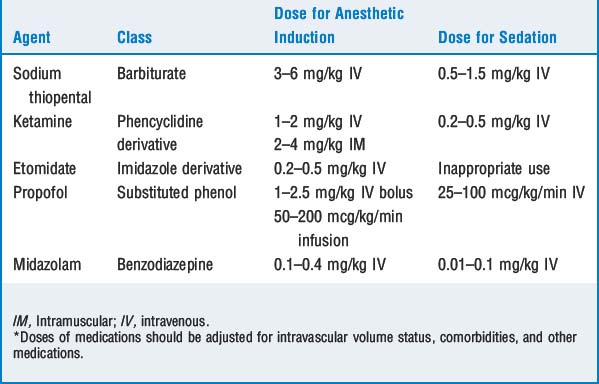
2 List the commonly used induction agents and their properties. Compare their cardiovascular effects
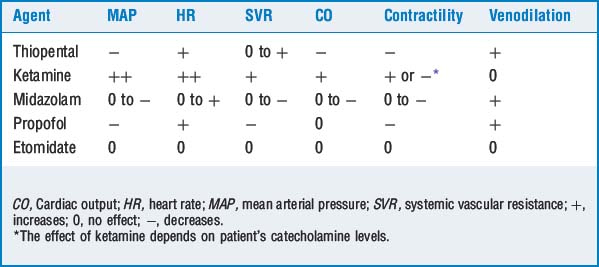
 Sodium thiopental (STP) is a direct myocardial depressant, produces peripheral vasodilation resulting in decreased mean arterial pressure (MAP), and produces a reflex tachycardia.
Sodium thiopental (STP) is a direct myocardial depressant, produces peripheral vasodilation resulting in decreased mean arterial pressure (MAP), and produces a reflex tachycardia. Etomidate is an imidazole derivative the induction properties of which result from Gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) receptor modulation. It is noted for its hemodynamic stability. Cardiac output (CO) and contractility are preserved, and only a mildly decreased MAP is noted. Side effects include pain on injection, nausea and vomiting, hiccups, myoclonus, seizures, thrombophlebitis, and most important, adrenal suppression.
Etomidate is an imidazole derivative the induction properties of which result from Gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) receptor modulation. It is noted for its hemodynamic stability. Cardiac output (CO) and contractility are preserved, and only a mildly decreased MAP is noted. Side effects include pain on injection, nausea and vomiting, hiccups, myoclonus, seizures, thrombophlebitis, and most important, adrenal suppression. Propofol: Myocardial depression and peripheral vasodilation are more profound than with thiopental and may result in a more significant decrease in MAP. There are minimal effects on heart rate (HR).
Propofol: Myocardial depression and peripheral vasodilation are more profound than with thiopental and may result in a more significant decrease in MAP. There are minimal effects on heart rate (HR). Ketamine: The sympathomimetic effects result in increased CO, MAP, and HR. It is a myocardial depressant, but usually its sympathomimetic properties dominate.
Ketamine: The sympathomimetic effects result in increased CO, MAP, and HR. It is a myocardial depressant, but usually its sympathomimetic properties dominate. Midazolam is the principal benzodiazepine used perioperatively. Benzodiazepines provide anxiolysis, sedation, amnesia, and in high doses unconsciousness. Midazolam has minimal myocardial depression. There is no effect on MAP or CO; HR may increase slightly.
Midazolam is the principal benzodiazepine used perioperatively. Benzodiazepines provide anxiolysis, sedation, amnesia, and in high doses unconsciousness. Midazolam has minimal myocardial depression. There is no effect on MAP or CO; HR may increase slightly. Opioids: High doses of most opioids have a vagolytic effect, producing bradycardia. The exception is meperidine, which has sympathomimetic effects that produce tachycardia. A decreased MAP may be noted secondary to bradycardia, vasodilatation, blockade of sympathetic response, and histamine release (especially evident with morphine and meperidine).
Opioids: High doses of most opioids have a vagolytic effect, producing bradycardia. The exception is meperidine, which has sympathomimetic effects that produce tachycardia. A decreased MAP may be noted secondary to bradycardia, vasodilatation, blockade of sympathetic response, and histamine release (especially evident with morphine and meperidine).These effects are noted when these medications are individually administered. When given in concert (e.g., midazolam followed by an opioid followed by pentothal), the effects are synergistic, and hemodynamic instability is not guaranteed (Tables 12-1 and 12-2).
3 Instead of injecting pentothal intravenously, you have inadvertently administered it into the patient’s intra-arterial line. What is the impact on the patient and how should potential problems be addressed?
4 What are contraindications to STP use?
 Thiopental allergy: STP contains a sulfur molecule that results in an increased risk of histamine release. Patients allergic to sulfates should not receive STP.
Thiopental allergy: STP contains a sulfur molecule that results in an increased risk of histamine release. Patients allergic to sulfates should not receive STP. Porphyria: Barbiturates increase porphyrin synthesis and may precipitate an acute porphyria attack with symptoms such as abdominal pain, weakness, autonomic dysfunction, and gastrointestinal and sleep disturbances.
Porphyria: Barbiturates increase porphyrin synthesis and may precipitate an acute porphyria attack with symptoms such as abdominal pain, weakness, autonomic dysfunction, and gastrointestinal and sleep disturbances.7 Discuss the concerns for the use of etomidate in the critically ill patient
KEY POINTS: Intravenous Anesthetics and Benzodiazepines 
10 What would be an appropriate induction agent for a 47-year-old healthy male with a parietal lobe tumor scheduled for craniotomy and tumor excision?
12 What benzodiazepines are commonly administered intravenously?
 Midazolam is lipid soluble and therefore has the most rapid onset and shortest duration of action. Unlike other benzodiazepines, midazolam is both lipid soluble and water soluble and therefore can be manufactured without the pain-inducing solvent propylene glycol. It has a single metabolite with minimal activity. It is by far the most common benzodiazepine used perioperatively.
Midazolam is lipid soluble and therefore has the most rapid onset and shortest duration of action. Unlike other benzodiazepines, midazolam is both lipid soluble and water soluble and therefore can be manufactured without the pain-inducing solvent propylene glycol. It has a single metabolite with minimal activity. It is by far the most common benzodiazepine used perioperatively.14 What do you tell the nurses who will monitor this patient about possible side effects of flumazenil?
1 Annane, et al. Etomidate and fatal outcome—even a single bolus dose may be detrimental for some patients. Br J Anaes. 2006;97:116-117.
2 Djillali A. ICU physicians should abandon the use of etomidate!. Intensive Care Med. 2005;31:325-326.
3 Wysowski D.K. Reports of death with use of propofol for nonprocedural (long-term) sedation and literature review. Anesthesiology. 2006;105:1047-1051.