CASE 115
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Cyst
B. Hematoma
C. Lipoma
D. Metastasis
2. What is the most likely location of the mass?
A. Pericardium
B. Myocardium
C. Left atrium
D. Right atrium
3. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Cyst
B. Hematoma
C. Lipoma
D. Metastasis
4. What is the most appropriate management?
A. No treatment
B. Chemotherapy
D. Surgery
ANSWERS
References
Hoey ET, Mankad K, Puppala S, et al. MRI and CT appearances of cardiac tumours in adults. Clin Radiol. 2009;64(12):1214–1230.
O’Donnell DH, Abbara S, Chaithiraphan V, et al. Cardiac tumors: optimal cardiac MR sequences and spectrum of imaging appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(2):377–387.
Cross-Reference
Cardiac Imaging: The REQUISITES, ed 3, p 281.
Comment
Clinical Features
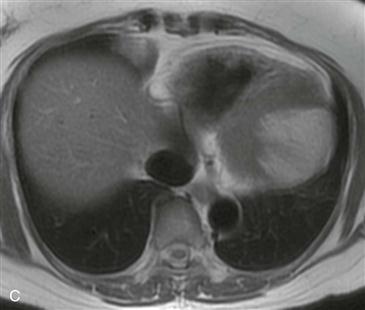
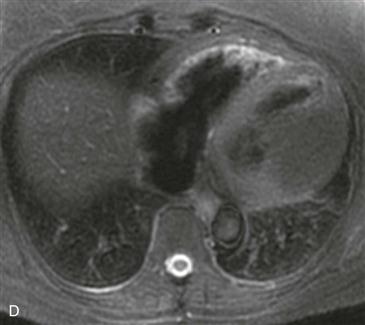
Cardiac lipoma is an uncommon benign encapsulated tumor that most commonly occurs in the right atrium. It is the second most common benign primary cardiac neoplasm after myxoma. Other locations include the epicardium, endocardium, interatrial septum, and left ventricle. Lipomas may grow into the pericardial space when they arise from the epicardium or into a ventricular chamber when they arise from the endocardium. Lipomas tend to be soft and flexible, and even large tumors may not compress the heart. Patients are usually asymptomatic. If there are symptoms of compression, such as pain or shortness of breath, surgical resection is usually performed.
Imaging Features
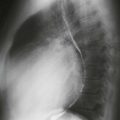
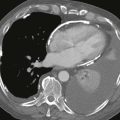
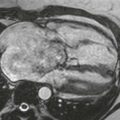
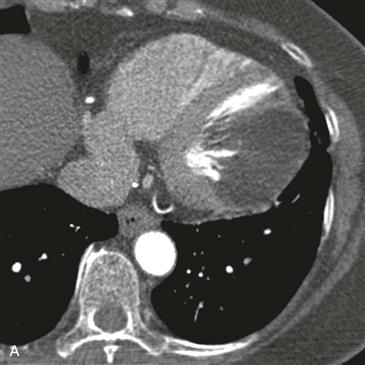
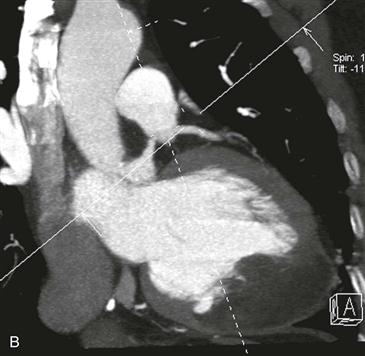
On CT, a cardiac lipoma manifests as a homogeneous, low-density mass with negative Hounsfield units (Figs. A and B). There is generally no enhancement, and there are no signs of invasion. MRI sequences with and without fat saturation can be used to show that the mass is composed of fat (Figs. C and D). It is important to differentiate cardiac lipoma from lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum, which has a bilobed appearance and is unencapsulated. Cardiac lipoma does not have significant fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake, whereas lipomatous hypertrophy may be FDG avid from associated brown fat.