TOPIC 10 Systemic vascular disease
Secondary hypertension
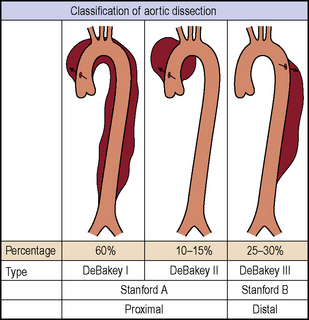
Table 10.1 Anatomical classification of thoracic aortic dissection
| Causes | Marker | Normal range |
|---|---|---|
| Kidney disease | Blood | |
| Creatinine | Men: | 45–90 μmol/L (0.5–1.0 mg/dl) |
| Women: | 60–110 μmol/L (0.7–1.2 mg/dl) | |
| Urine output | ||
| GFR | Men: | < 70 ml/min/m2 |
| Women: | < 60 ml/min/m2 | |
| Cushing’s syndrome | Dexamethasone suppression test | |
| Cortisol | N/A | |
| ACTH | N/A | |
| Phaeochromocytoma | 24-hour urine | |
| Epinephrine | 0.5–20 μg/24 hours | |
| Norenephrine | 15–80 μg/24 hours | |
| Dopamine | 65–400 μg/24 hours | |
| Renin | 20–100 mU/L | |
| Conn’s syndrome | Low renin | <20 |
| Aldosterone/renin ratio | >750 | |
| Hyperthyroidism | TSH | 0.3–3.0 mIU/L |
| Thyroxine (T4) | 4–11 μg/dl | |
| T3 | 130–220 ng/dl |
GFR = glomerular filtration rate, ACTH = adrenocorticotrophic hormone, TSH = thyroid stimulation hormone.