Etodolac (Lodine)
CLASSIFICATION
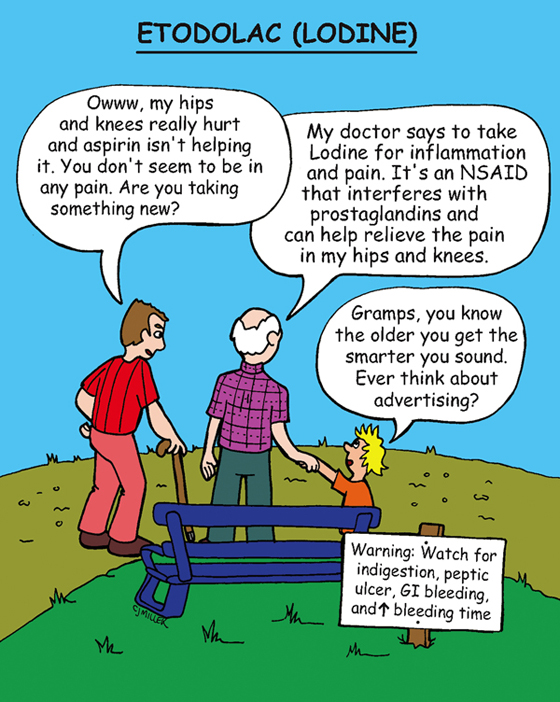
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory analgesic
ACTIONS
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis and produces analgesic and antiinflammatory effects. These actions will reduce the intensity of the pain stimulus reaching sensory nerve endings.
USES
• Acute long-term treatment of pain associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Active peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal (GI) ulceration, chronic inflammation of GI tract, GI bleeding disorders
• Impaired renal and hepatic function
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Indigestion,** dizziness, headache, abdominal pain or cramps, diarrhea, nausea
• Causes less GI irritation and bleeding tendencies than other NSAIDs
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. Assess joints for pain and signs of inflammation.
2. Inspect affected joints for level of mobility.
3. *Monitor complete blood count and liver and renal function.*
4. *Observe for bleeding or bruising.*
5. ‡Teach the patient to swallow the capsules whole and not to crush or chew.‡
6. ‡Teach the patient not to take aspirin or alcohol during therapy.‡
Antigout Agents: febuxostat (Uloric), allopurinol (Zyloprim), probenecid (Benemid)
ACTIONS
Inhibit the infiltration and phagocytosis of leukocytes, thus decreasing the breakdown of uric acid to urate crystals. Deposition of urate crystals causes pain and inflammation.
USES
• Long-term treatment of acute gouty arthritis; is not useful in the treatment of an acute attack of gouty arthritis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Severe gastrointestinal (GI) disorders
• Cardiac, hepatic, or renal disorders
SIDE EFFECTS
• febuxostat (Uloric): **Nausea, arthralgia,** rash, and abnormal liver function studies
• probenecid: **Vomiting,** diarrhea, anorexia; renal deposits of urate may cause damage
• allopurinol (Zyloprim): GI symptoms, drowsiness, headache, abdominal cramping; toxicity—†hypersensitivity syndrome† with **rash,** fever, eosinophilia, and liver and renal malfunction
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Hyperuricemic agents are given to prevent an attack; is not effective for an acute attack.*
2. *Initially, symptoms may get worse until uric acid levels are decreased.*
3. *Antigout agents can be given with food and milk to decrease GI discomfort.*
4. ‡Patient should avoid beer, ale, and wine because they may cause sudden gout attack.‡
5. *Encourage an increase intake of fluids to increase excretion of uric acid and to decrease concentration.*
6. ‡Teach patient to avoid smoked meats and high-protein diets.‡
Bisphosphonate Therapy alendronate (Fosamax), risedronate (Actonel), ibandronate (Boniva) zoledronate (Reclast)
CLASSIFICATION
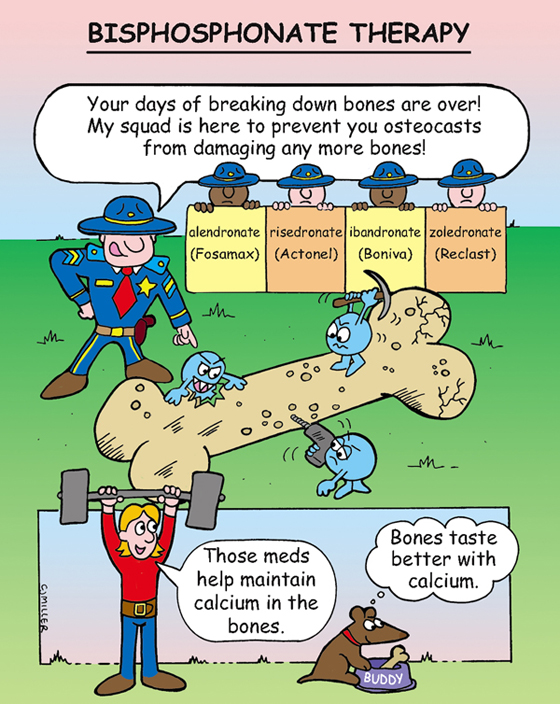
Bisphosphonate, bone-resorption inhibitor
ACTIONS
Is incorporated into the bone and inhibits bone resorption by decreasing activity of osteoclasts; provides significant increase in bone mineral density.
USES
• Prevents and treats the progression of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Gastrointestinal (GI) irritation, esophageal disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and renal function impairment
• Patients with swallowing disorders
SIDE EFFECTS
• Oral medications—esophagitis, **GI irritation and discomfort, back pain**
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. ‡Oral medications—patient should take each tablet or oral solution in the morning with a full glass of water (6 to 8 oz) at least 30 to 60 minutes before the first food, beverage, or medication of the day. Orange juice, coffee, or food significantly decreases effectiveness.‡
2. ‡Patient should not chew or suck on the tablet.‡
3. ‡After taking medication, patient should remain upright (sitting or standing) for 30 to 60 minutes. Patient should not lie down until after eating.‡
4. ‡Patient should not take medication at bedtime or at the same time as other medications (including aspirin, antacids, or calcium supplements). Patient should wait at least 30 minutes before taking any other drug.‡
5. ‡Boniva is taken once a month; however, above precautions are still necessary on administration.‡