CHAPTER 10 CARDIOLOGY
PRIMARY PREVENTION OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE
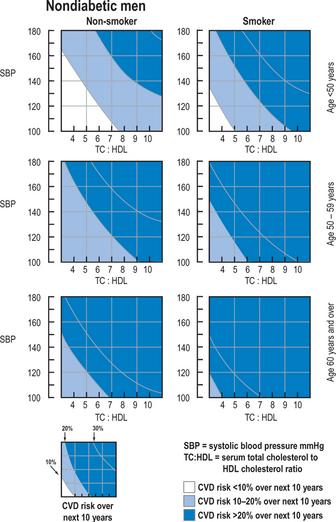
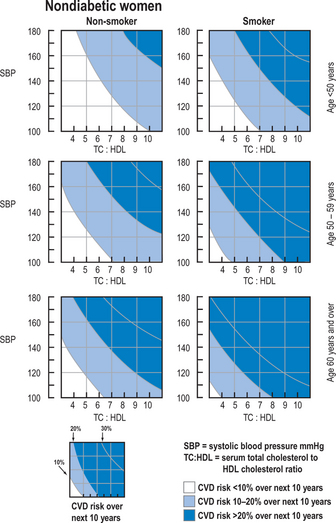
In order to calculate a patient’s CVD risk the following information is required:
Apply this information to the graphs on pp. 147–148 to calculate the 10-year risk of developing CVD. Alternatively, use the computer CHD/CVD risk calculator in the clinical system holding the patient’s medical record.
HYPERTENSION
Diagnosis
The new hypertensive.
After the fourth BP reading
Management
Prescribing
Follow-up
CHOLESTEROL
Diagnosis
Management
Advice.
(Send the patient to the practice nurse for advice.)
CHEST PAIN
Diagnosis
History.
If the history suggests MI, aneurysm, PE or a very ill patient, admit the patient to hospital by ambulance on 999 without delay (see p. 158).
Examination
Investigations
A therapeutic trial of either a PPI or a nitrate/beta-blocker is then justified, e.g.:
The choice is governed by the ‘best guess’ based on the history and examination so far.
ANGINA
Angina is pain due to myocardial ischaemia.
STABLE ANGINA
Management
Advice.
See general lifestyle advice (p. 146). Warn the patient to report any increase in chest pain immediately.
Prescribing
ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (MI)
Diagnosis
Investigations
Immediate management of suspected MI
POSTMYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
HEART FAILURE
Diagnosis
There are two aspects: diagnosing heart failure and diagnosing its cause.
History.
RAYNAUD’S PHENOMENON
FUNNY TURNS
Syncope is characterised by transient loss of consciousness, with or without a fall. Simple vasovagal faints are the commonest cause of syncope in young patients. The phrase ‘funny turn’ is often used by patients and relations to describe a wide variety of symptoms, which include syncope (see dizziness, p. 274).
The causes can be divided as follows.
Diagnosis
History.
PALPITATIONS
Management
Treatment.
The following are treatable in general practice.
Constant atrial fibrillation.
Anticoagulate with warfarin, over the age of 50, unless there are contraindications, in which case give aspirin, 75 mg daily (see p. 330).
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Anticoagulate if there are no contraindications; otherwise give aspirin. Digoxin is of no benefit.