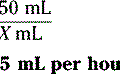CHAPTER 3 Compounding
The Federal Drug Administration (FDA) defines traditional pharmacy compounding as “the combining, mixing, or altering of ingredients to create a customized medication for an individual patient in response to a licensed practitioner’s prescription (www.fda.gov). Compounding is often used when the patient is intolerant of a manufactured drug. It may also be needed when an alternative route of administration is needed and not available commercially. It also allows physicians to prescribe customized strengths and dosage systems.
| Binders | |
| Buffer | |
| Coatings | |
| Coloring agents | |
| Diluents/Fillers | |
| Emulsifiers | |
| Flavoring agents | |
| Preservatives | |
| Antioxidants | |
| Alcohols | |
| Parabens | |
| Chelators | |
| Sweeteners |
| Aliquot | A stock product made for a quantity below the least measurable quantity; see also least measurable quantity |
| Aseptic technique | The process of making a sterile product while reducing contamination of any particles, pathogens, or pyrogens; particularly important for parenteral, ophthalmic, and inhaled preparations |
| Biologic safety cabinet | A work area designed to aseptically prepare sterile medications; the vertical flow hood is ideal for preparing chemotherapeutic drugs, volatile substances, and other cytotoxic medications; the horizontal flow provides no protection to the user |
| Eutectic mixture | The combination of two solid substances at room temperature, which become liquid when combined |
| Geometric dilution | Mixing two powders of unequal size |
| Infusion (herbal medicine) | The steeping of a medicine in water; making a tea |
| Infusion (modern medicine) | Continuous delivery of a solution over a prolonged period of time |
| Least measurable quantity | The smallest amount that can be quantified by a scale or other measuring device; if a quantity must be used for which the device cannot measure, an aliquot must be made |
| Levigate | To make into a smooth, fine powder or paste, as by grinding when moist |
| Liniment | A liquid or semifluid preparation that is applied to the skin as a counterirritant |
| Mortar | A bowl for grinding and mixing ingredients |
| Muddle | The process of grinding a solid in a mortar with a pestle into a fine powder |
| Pestle | A rod used to grind and mix ingredients |
| Spatulation | Blending small amounts of powder by movement of a spatula on a paper or tile |
| Topical | A dosage form meant to treat an affected area without systemic effects |
| Transdermal | A medicated adhesive patch that is placed on the skin to deliver a time-released dose of medication through the skin and into the bloodstream; not to be confused with a topical medication |
| Triturate | To rub, crush, grind, or pound into fine particles or a powder; pulverize; also known as muddling |
REVIEW QUESTIONS
(Answers and Rationales on page 317.)
How many milligrams of sodium fluoride are required to prepare the prescription?
How much of each ingredient are needed to prepare this prescription.