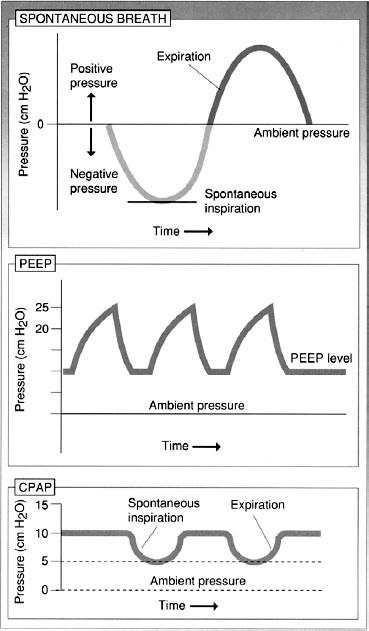
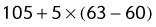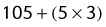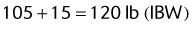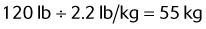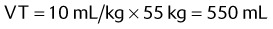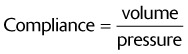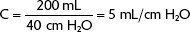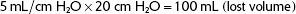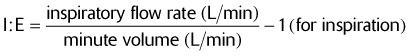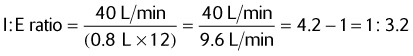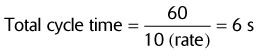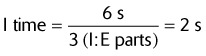CHAPTER 11 VENTILATOR MANAGEMENT
PRETEST QUESTIONS
1. The following information has been obtained from a ventilator patient.
| Peak inspiratory pressure | 48 cm H2O |
| Plateau pressure | 27 cm H2O |
| VT | 850 mL |
| PEEP | 4 cm H2O |
2. A volume-cycled ventilator is in the control mode and the I:E inspiratory/expiratory ratio alarm is sounding. Which control adjustment would correct this problem?
3. Mechanical ventilation can lead to which of the following complications?
4. Static lung compliance will decrease as a result of which of the following?
5. These data have been collected from a patient whose ventilator was in the control mode.
To increase this patient’s PaCO2 to 40 mm Hg, the ventilator rate should be adjusted to what level?
6. The following data have been collected from a patient using a volume ventilator in the control mode.
REVIEW
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA6a-b, IIA11a, d, IIID2c, IIID10, IIIF2i6,9, IIIG3f,i,k, l
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA2a-b, IIID2c, IIID8, IIIF2e6, IIIG3f,h,k
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIID2b,d, IIIF2i1-5,11, IIIG3a-e
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IIID2b,d, IIIF2e1,2,3,4,5,9, IIIG3a-e
106 + [6 × (height in inches − 60 in)]
105 + [5 × (height in inches − 60 in)]
EXAMPLE:
Set VT at 200 mL (0.2 L). Peak pressure reached is 40 cm H2O.
This means that once the patient has started using the ventilator, 5 mL of the set tidal volume will be lost in the tubing for every 1 cm H2O registering on the manometer.
EXAMPLE:
Tubing compliance, 5 mL/cm H2O
Peak inspiratory pressure, 20 cm H2O
EXAMPLE:
Calculate the inspiratory time if the I:E ratio is 1 : 2 and the ventilator rate is 10/min.